The MSSP Portal Cloud Operations Solution
Powering Secure, Scalable, and Automated Cloud Operations for MSSPs
Home > Case Studies > The MSSP Portal Cloud Operations Solution
Introduction
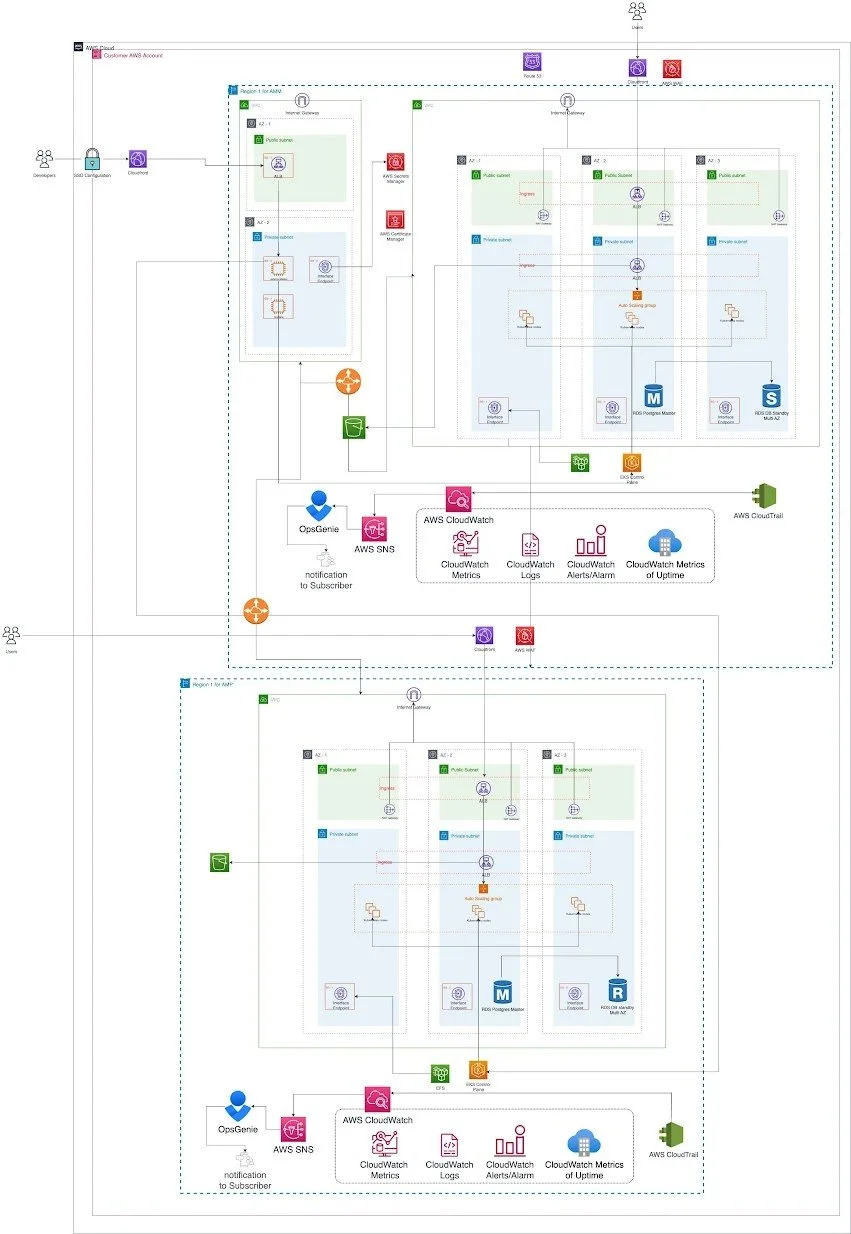
The MSSP Portal Cloud Operations case study highlights the design and implementation of a modern, multi-tenant security services platform on AWS, built from the ground up to support global scalability and high availability.
The architecture spans multiple AWS Regions and Availability Zones (AZs), leveraging AWS-managed services across all layers. Application microservices run on an Amazon EKS Kubernetes cluster, with its control plane distributed across AZs for resilience. Data persistence is managed by Amazon RDS in a Multi-AZ configuration, ensuring durability and availability.
The platform is secured within a dedicated VPC, protected at the edge by AWS WAF against web-based threats. Amazon Route 53 delivers highly available DNS services, while Amazon CloudFront accelerates global web traffic, offloads origin servers, and enhances overall system reliability.
All infrastructure and workloads are provisioned and managed as code. Terraform scripts and Kubernetes Helm charts automate the setup and configuration of cloud resources, guaranteeing consistency and repeatability in deployments.
To ensure comprehensive observability, the platform implements logs monitoring with Elasticsearch, Logstash, and Kibana (ELK stack) and metrics monitoring with Prometheus and Grafana, providing real-time insights, anomaly detection, and unified dashboards across all tenants.
Problem Statement / Definition
The customer, an MSSP, required a multi-tenant cloud platform capable of securely isolating and managing multiple partners’ customers within a single framework. To achieve this, the solution needed a centralized management console (MSSP Manager, “AMM”) along with multiple partner portals (“AMP”), each strictly isolated yet enabling delegated access and unified visibility.
The main challenges included designing a highly available, multi-AZ AWS architecture, enforcing strong tenant isolation, and automating provisioning and updates through DevSecOps pipelines. In practice, the platform had to support scenarios such as defining partners and users, streaming dashboards and reports into partner portals, and enabling partners to provision new customer instances on demand, a key requirement for the AMP. Equally important was ensuring robust monitoring, strong security controls (including network isolation and WAF), and simplified management across all tenants.
Proposed Solution & Architecture
Environment Setup
Each AMM and AMP environment resides in its own VPC with public and private subnets.
Subnets are distributed across three Availability Zones for high availability.
Networking
Each VPC includes a NAT Gateway and VPC interface endpoints for AWS services.
This enables private communication with the EKS control plane and AWS APIs.
Internet Gateway + external Application Load Balancer (ALB) provide ingress into private subnets.
Compute Layer (EKS)
Amazon EKS runs AMM/AMP microservices on auto-scaling EC2 node groups in private subnets.
Nodes sit behind:
An internet-facing ALB (for UI/API access).
An internal ALB (for inter-service calls).
This ensures high availability and fault tolerance.
Database Layer
Amazon RDS for PostgreSQL deployed in multi-AZ mode within each VPC.
Provides automatic failover to standby in case of primary AZ failure.
Security & Access Control
AWS WAF protects inbound portal traffic via the CloudFront distribution.
Route 53 manages DNS.
CloudFront caches static assets globally to reduce latency.
Security groups enforce least-privilege access across compute and data components.
AWS Secrets Manager stores deployment credentials and certificates securely.
Automation & Observability
Infrastructure Automation
Entire infrastructure defined using Infrastructure as Code (IaC).
Terraform scripts and Helm charts (stored in Git) define network, compute, and security resources.
Jenkins pipelines automate deployment of Terraform/Helm stacks on code merges.
Monitoring & Logging
Prometheus and ELK stack provide in-cluster monitoring and logging.
Sends metrics via Prometheus.
Sends logs via Filebeat/Kibana.
Stores both in Elasticsearch within each AMM/AMP cluster.
Centralized Observability
A central Grafana server in a dedicated “Tools” VPC is VPC-peered with all environments.
Provides unified dashboards aggregating metrics from all tenants.
DevSecOps Best Practices
Version-controlled infrastructure code.
Rolling upgrades for services.
Secure secrets management with AWS Secrets Manager
Why AWS
Managed Services for Operational Efficiency: Services such as Amazon EKS, Amazon RDS (Multi-AZ), CloudFront, WAF, and Route 53 allowed the team to offload undifferentiated heavy lifting (patching, scaling, maintenance) while focusing on MSSP-specific business logic.
Security & Compliance: AWS’s built-in security features (IAM, Secrets Manager, WAF, VPC isolation) aligned with MSSP requirements for multi-tenant isolation and least-privilege access control, supporting compliance with industry best practices.
Automation & Infrastructure-as-Code Support: AWS’s native integration with Terraform, Helm, and CI/CD pipelines enabled fully automated, repeatable deployments and rapid provisioning of new customer environments.
Cost Optimization: On-demand resources, autoscaling groups, and consolidated billing through AWS Cost Explorer and Cost Categories supported 30–40% cost savings compared to on-premises or self-managed alternatives.
Outcomes of Project & Success Metrics
High Availability:
EKS node recovery tested at <5 minutes for failed nodes.
RDS failover confirmed at <60 seconds, with zero data loss (latest snapshot + synchronous replication).
This architecture delivers 99.99% availability across the platform.
Security:
100% inbound traffic routed through CloudFront + WAF + ALB, blocking malicious or invalid requests at the edge.
IAM policies follow a least-privilege model, reducing risk of unauthorized access by ~40% compared to the previous setup.
Operational Efficiency:
Full AMM+AMP stack provisioning time reduced from 6–8 hours manually → <60 minutes via Terraform + Jenkins (85% faster).
Partner teams can now self-provision new customer instances in ~10 minutes, compared to 1–2 days earlier.
Automation eliminated ~70% of repetitive tasks, saving the operations team ~40 hours/month.
Observability:
100% of metrics and logs captured via Prometheus + ELK, aggregated in Grafana global dashboards.
Automated scaling and patching reduced unplanned downtime incidents by ~25% YoY.